The novel coronavirus’ spike protein plays additional key role in illness
The novel coronavirus’ spike protein plays additional key role in illness
Salk researchers and collaborators show how the protein damages cells, confirming COVID-19 as a primarily vascular disease
LA JOLLA—Scientists have known for a while that SARS-CoV-2’s distinctive “spike” proteins help the virus infect its host by latching on to healthy cells. Now, a major new study shows that the virus spike proteins (which behave very differently than those safely encoded by vaccines) also play a key role in the disease itself.
The paper, published on April 30, 2021, in Circulation Research, also shows conclusively that COVID-19 is a vascular disease, demonstrating exactly how the SARS-CoV-2 virus damages and attacks the vascular system on a cellular level. The findings help explain COVID-19’s wide variety of seemingly unconnected complications, and could open the door for new research into more effective therapies.
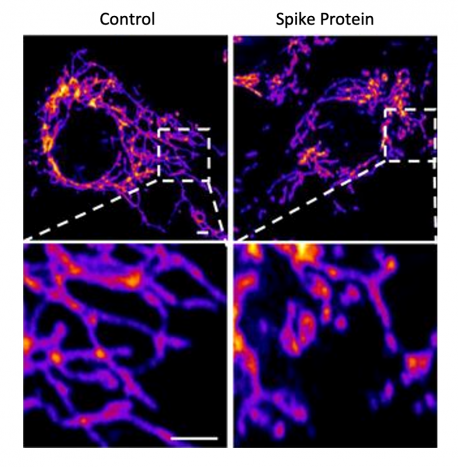
Click here for a high-resolution image.
Credit: Salk Institute
“A lot of people think of it as a respiratory disease, but it’s really a vascular disease,” says Assistant Research Professor Uri Manor, who is co-senior author of the study. “That could explain why some people have strokes, and why some people have issues in other parts of the body. The commonality between them is that they all have vascular underpinnings.”
Salk researchers collaborated with scientists at the University of California San Diego on the paper, including co-first author Jiao Zhang and co-senior author John Shyy, among others.
While the findings themselves aren’t entirely a surprise, the paper provides clear confirmation and a detailed explanation of the mechanism through which the protein damages vascular cells for the first time. There’s been a growing consensus that SARS-CoV-2 affects the vascular system, but exactly how it did so was not understood. Similarly, scientists studying other coronaviruses have long suspected that the spike protein contributed to damaging vascular endothelial cells, but this is the first time the process has been documented.
In the new study, the researchers created a “pseudovirus” that was surrounded by SARS-CoV-2 classic crown of spike proteins, but did not contain any actual virus. Exposure to this pseudovirus resulted in damage to the lungs and arteries of an animal model—proving that the spike protein alone was enough to cause disease. Tissue samples showed inflammation in endothelial cells lining the pulmonary artery walls.
The team then replicated this process in the lab, exposing healthy endothelial cells (which line arteries) to the spike protein. They showed that the spike protein damaged the cells by binding ACE2. This binding disrupted ACE2’s molecular signaling to mitochondria (organelles that generate energy for cells), causing the mitochondria to become damaged and fragmented.
Previous studies have shown a similar effect when cells were exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but this is the first study to show that the damage occurs when cells are exposed to the spike protein on its own.
“If you remove the replicating capabilities of the virus, it still has a major damaging effect on the vascular cells, simply by virtue of its ability to bind to this ACE2 receptor, the S protein receptor, now famous thanks to COVID,” Manor explains. “Further studies with mutant spike proteins will also provide new insight towards the infectivity and severity of mutant SARS CoV-2 viruses.”
The researchers next hope to take a closer look at the mechanism by which the disrupted ACE2 protein damages mitochondria and causes them to change shape.
Other authors on the study are Yuyang Lei and Zu-Yi Yuan of Jiaotong University in Xi’an, China; Cara R. Schiavon, Leonardo Andrade, and Gerald S. Shadel of Salk; Ming He, Hui Shen, Yichi Zhang, Yoshitake Cho, Mark Hepokoski, Jason X.-J. Yuan, Atul Malhotra, Jin Zhang of the University of California San Diego; Lili Chen, Qian Yin, Ting Lei, Hongliang Wang and Shengpeng Wang of Xi’an Jiatong University Health Science Center in Xi’an, China.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shaanxi Natural Science Fund, the National Key Research and Development Program, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University; and Xi’an Jiaotong University.
DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902
